The role of business leaders has become increasingly challenging in recent years. CEOs have had to navigate a global pandemic, supply chain disruptions, geopolitical instability, inflation, and more.
To build resilience for the future, organisations must stay ahead of emerging technologies that can transform entire industries.
That's where quantum computing comes in. As Mary Barra, CEO of General Motors notes, "Quantum computing has the potential to reshape every industry. From material science and logistics to finance and healthcare, the applications are endless."
Quantum computers have the potential to optimise entire supply chains in real time and design new materials at a fraction of the cost using simulation and machine learning.
However, quantum computing remains mysterious to many business leaders. They recognize its world-changing potential but don't understand how it works or what practical benefits it could deliver.
This article aims to demystify quantum computing and discuss how organisations can start integrating it into their businesses today. We'll explain the basics of how quantum computers operate, explore promising applications, and provide tangible steps leaders can take to begin leveraging this powerful emerging technology.
Quantum computing has the potential to reshape every industry. From material science and logistics to finance and healthcare, the applications are endless.
Mary Barra, CEO of General Motors
What is Quantum Computing?
Let's start by defining quantum computing in terms of its operation and its underlying principles. Quantum computing uses quantum mechanics techniques to execute calculations tenfold quicker than classical computers. Traditional computers utilise bits that are either 0s or 1s, whereas quantum computers use quantum bits or qubits that can be 0s, 1s, or both at the same time due to a property known as superposition. This enables quantum computers to simultaneously analyse all possible solutions to a problem.
Put simply, visualise a maze. Finding the exit would need a classical computer to attempt each path one at a time. In contrast, a quantum computer could explore every option at once, which would enable it to solve the problem considerably more quickly.
Quantum Computing as a service
While building quantum computers requires significant technological and financial resources, Quantum Computing as a Service (QCaaS) lowers the barriers to entry.
Pioneers in the field like IBM and Google have established quantum cloud platforms, giving businesses access to this emerging processing power without the need for expensive infrastructure or specialised in-house talent.
Through QCaaS, organisations can now tap into quantum computing capabilities via the cloud. This allows CEOs to initiate pilot projects exploring practical applications and integrate initial quantum solutions.
Businesses can upskill their workforce by training employees on quantum algorithms, programming, and software using cloud-based resources.
By leveraging QCaaS, even organisations without quantum expertise can start experimenting with the technology. This hands-on approach helps identify promising use cases and lays the groundwork for more advanced adoption down the line.
Organisations should understand the types of challenges that quantum computing can solve and how they relate to the organisation's strategic goals.
Use cases for Quantum Computers
Let's take a closer look at some possible and even existent business use cases for quantum computing. Consider how any of these functions can help you drive business value if you're exploring quantum computing for your corporation.
Developing new products
By quickly evaluating large datasets about consumer preferences, market trends, and design aesthetics, quantum computing can speed up the product development process. This makes it possible for companies to provide a wide range of choices, attributes, and suggestions for new items.
Optimising supply chain
Quantum algorithms could aid firms in real-time optimization of complex supply chain networks by discovering efficient shipping routes and inventory levels. This could result in decreased prices and carbon footprints.
Improving database efficiency
Quantum computing can improve database efficiency by rapidly detecting and removing duplicate data, sorting and categorising information, maximising data discovery, and assuring effective data governance, particularly in decentralised data environments.
Securing data
Quantum-safe encryption techniques have the potential to protect data and critical infrastructure from future hacking threats that exceed traditional computing capabilities.
Machine Learning acceleration
Quantum computers have the potential to greatly accelerate the training of machine learning algorithms. This time-saving advantage opens up more chances for machine learning research and applications, contributing to developments in artificial intelligence.
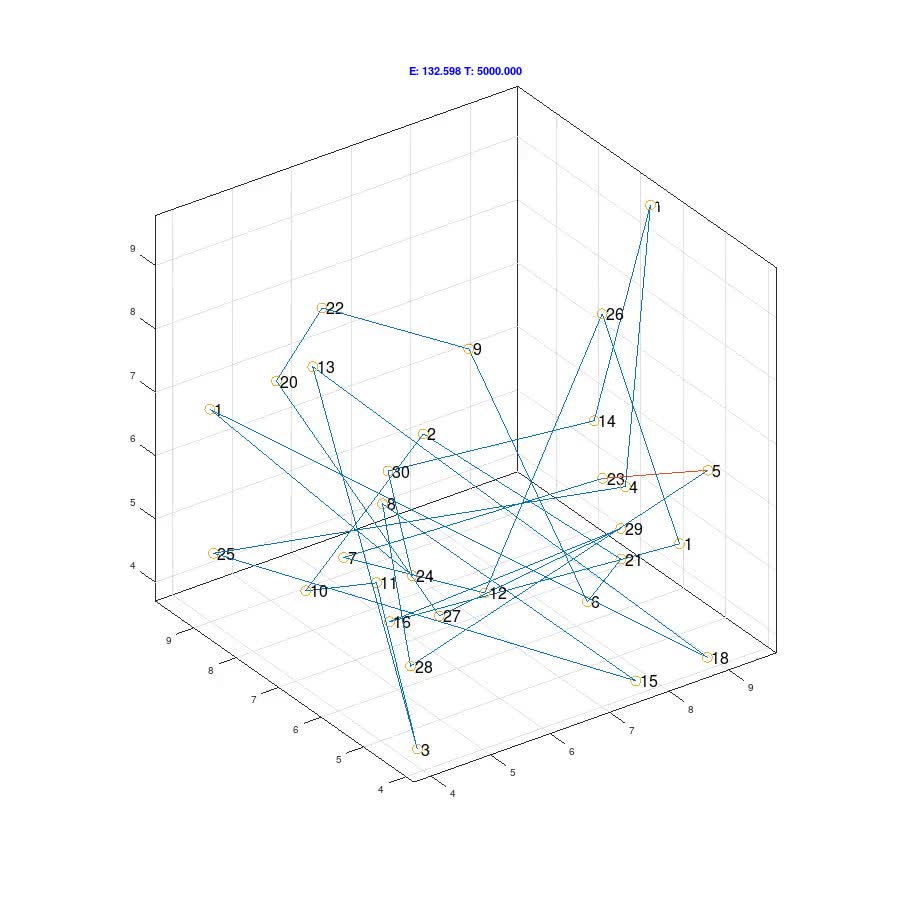
3D Travelling Salesman Problem solved | Panchotera~enwiki (talk | contribs)
Optimised problem solving
Quantum computers outperform classical computers in addressing complicated optimization problems at a much faster rate. This is especially useful for tackling issues like the travelling salesman dilemma, which has ramifications across multiple corporate areas.
Improving customer service
Quantum machine learning may offer a richer, more accurate contextual understanding of client needs, wants, and behaviours in real time. This enhanced customer care could increase personalization and responsiveness.
Practical tips for organisations
Organisations should perform a thorough assessment of the quantum potential within their industry and operational context before jumping into quantum computing deployment. Understand the types of challenges that quantum computing can solve and how they relate to the organisation's strategic goals.
Pilot quantum projects
Embarking on quantum projects requires a blend of strategic planning, skilled resources, and a willingness to experiment and learn. As the field is rapidly evolving, flexibility and continuous learning are key to successfully piloting quantum projects.
Here are some practical steps:
- Educate and build awareness through developing internal workshops and training and engaging with quantum computing experts to gain deeper insights and guidance.
- Identify Potential Use Cases by analysing areas within your organisation where quantum computing could offer significant advantages (e.g., complex simulations, optimisation problems, cryptography).
- Set realistic goals by focus on what can be achieved and align with your organisation's long-term strategy.
- Partner with Quantum Computing Providers such as IBM, Google, and Microsoft. This can provide access to quantum hardware and mature software tools.
- Conduct small, Controlled Experiments to test and learn from quantum algorithms and hardware.
- Focus on Quantum-Safe Cybersecurity and Prepare for Quantum Threats by developing strategies to protect against future quantum computing threats, especially in cryptography (i.e., Quantum-resistant algorithms and encryption methods).
- Plan for scaling as quantum technology matures.
While quantum computing is still in its early stages, strategic firms may engage with the technology now and position themselves for a competitive advantage when practical applications arise in the future years.
Stay informed and collaborate
Because of the rapid advancement of quantum computing, staying up to date on the latest advances is critical. Form alliances with quantum computing research labs, industry professionals, and technology providers. Participating in a knowledge-sharing network ensures access to cutting-edge breakthroughs and assists enterprises in navigating the complicated environment of quantum technology.
Invest in workforce training
Building internal expertise is critical for the effective deployment of quantum computing. Invest in training programs to provide your workers with the skills necessary for developing quantum algorithms, and programming languages, and comprehending the unique laws of quantum mechanics. Creating a quantum-ready workforce in-house assures that the firm can effectively use this disruptive technology.
Identify applicable use cases
Not all business problems may benefit from quantum computing. Identify specific use cases where quantum capabilities connect with company goals and provide a significant advantage. Understanding the relevance of quantum computing ensures focused and strategic implementation, optimising the impact on operational efficiency and innovation.
In summary, while quantum computing is still in its early stages, strategic firms may engage with the technology now and position themselves for a competitive advantage when practical applications arise in the future years. With continuing progress, quantum computing could eventually revolutionise operations in a variety of industries.